Psychedelics are compounds that produce an atypical state of consciousness characterized by altered perception, cognition, and mood. Psychedelics are emerging as promising treatments for a range of neuropsychiatric disorders including depression, substance use disorder, and post-traumatic stress disorder. For example, psilocybin-assisted psychotherapy has been shown efficacious for treating major depression in Phase II trials. A notable feature is the long-lasting benefit: after one or two dosing sessions, reduction of depressive symptoms was durable for weeks and up to several months. Given these exciting early results, psychedelics as medicine have the potential to transform psychiatry. Yet we know very little about how psychedelics modify brain structure and function, fundamental scientific knowledge that can ensure safe and effective use in the clinic.
Cornell is leading the resurgence to understand the basic neurobiology of psychedelics. Collectively, we discovered that a single dose of psilocybin leads to long-lasting rewiring of neuronal connections. We found that LSD and psilocybin flatten neural dynamics to facilitate switches of brain states. We identified key components of the neural circuit that mediates the long-term effects of psilocybin.

Collaborating Faculty Members
Ongoing projects leverage a broad community of researchers at Cornell including Cornell Neurotech and Weill Cornell Medicine. Our goal is to gain a deep understanding for how psychedelics impact brain circuits to exert their remarkable short- and long-term behavioral effects. Researchers include:
Projects
-
Impact of psilocybin on cerebral blood flow
Psychedelics act on serotonin receptors, which are present in blood vessels. The goal of this project is to measure the effects of psilocybin on cerebral blood flow and neurovascular coupling in mice using high-resolution optical imaging methods. The results will tell us how psychedelics influence hemodynamic response, which is critical for interpreting signals in human neuroimaging studies such as fMRI.
-
Novel technologies to visualize psilocybin’s plasticity actions
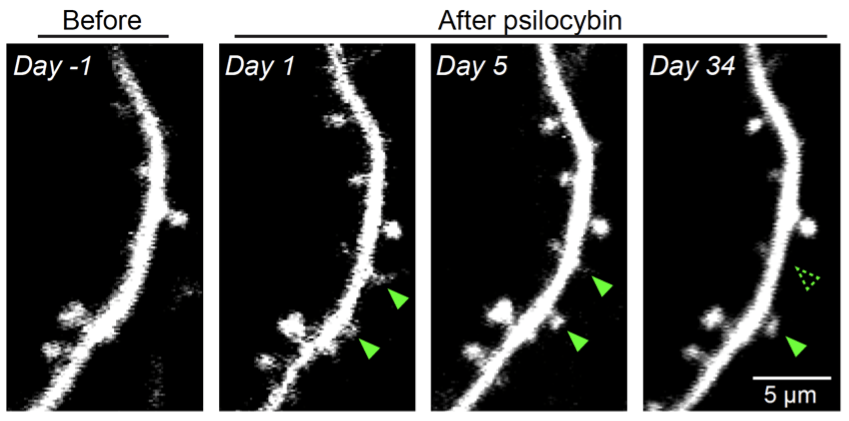
Our prior work shows that a single dose of psilocybin can lead to enduring increases in neuronal connections in the frontal cortex. This project seeks to extend those findings, by developing a novel optical microscopy method that will enable precise measurement of psilocybin-evoked plasticity over a much greater extent of the brain circuitry and over longer time periods.
-
Effects of psilocybin on social behavior and learning
A key challenge to studying psychedelics in animal models is the lack of suitable behavioral assays. Cornell researchers have innovated a new paradigm for measuring social behavior and complex learning in mice. The approach allows for researchers to examine neural correlates of learning as animals form spatial and social memories that are shaped by psychedelics.
-
Molecular signals responsible for therapeutic effects of ketamine and psilocybin
Neural rewiring in the brain likely underpins the long-term beneficial effects of psychedelics, however the molecular signals that initiate the plasticity processes remain unidentified. Using single-cell sequencing and spatial transcriptomics, we are determining the specific molecules in neurons that are essential for kickstarting psychedelics’ effects on neural plasticity.
In the Media
Cornell News (2025): Hitting the target: imaging reveals psilocybin’s neural odyssey
Cornell News (2024): Psychedelics excite cells in hippocampus to reduce anxiety
Cornellians (2024): Digital artist dreams his creations in pixels and neurons
Weill Cornell Medicine Newsroom (2022): Psychedelic drugs flatten the brain’s dynamic landscape








